3.8 Transformation Geometry
Transformation geometry involves moving, rotating, reflecting, enlarging, or shearing objects while preserving certain properties.Key Concepts:
-
Translation:
Moving a shape without rotating or resizing it. A translation is represented as: \[ \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix} \to \begin{pmatrix} x + a \\ y + b \end{pmatrix} \] where \((a, b)\) is the translation vector. -
Rotation:
Turning a shape around a fixed point (center of rotation). A rotation by \(90^\circ\) counterclockwise about the origin transforms a point \((x, y)\) to: \[ (x', y') = (-y, x). \] -
Reflection:
Flipping a shape over a line (mirror line). Common reflections include: \[ \text{Reflection over } y = 0 \Rightarrow (x, y) \to (x, -y) \] \[ \text{Reflection over } x = 0 \Rightarrow (x, y) \to (-x, y) \] -
Enlargement:
Resizing a shape by a scale factor \(k\) about a center \((a, b)\). The transformation is: \[ \begin{pmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} a + k(x - a) \\ b + k(y - b) \end{pmatrix} \] -
Shear:
A transformation that distorts a shape along a particular axis while keeping one line fixed. Horizontal shear is given by: \[ \begin{pmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x + ky \\ y \end{pmatrix} \] where \(k\) is the shear factor.
Examples:
Example 1: Find the image of the point \((3, 4)\) under the translation \(\begin{pmatrix} -2 \\ 5 \end{pmatrix}\).
Solution:
Step 1: Apply the translation rule. \[ (x', y') = (3 - 2, 4 + 5) = (1, 9). \]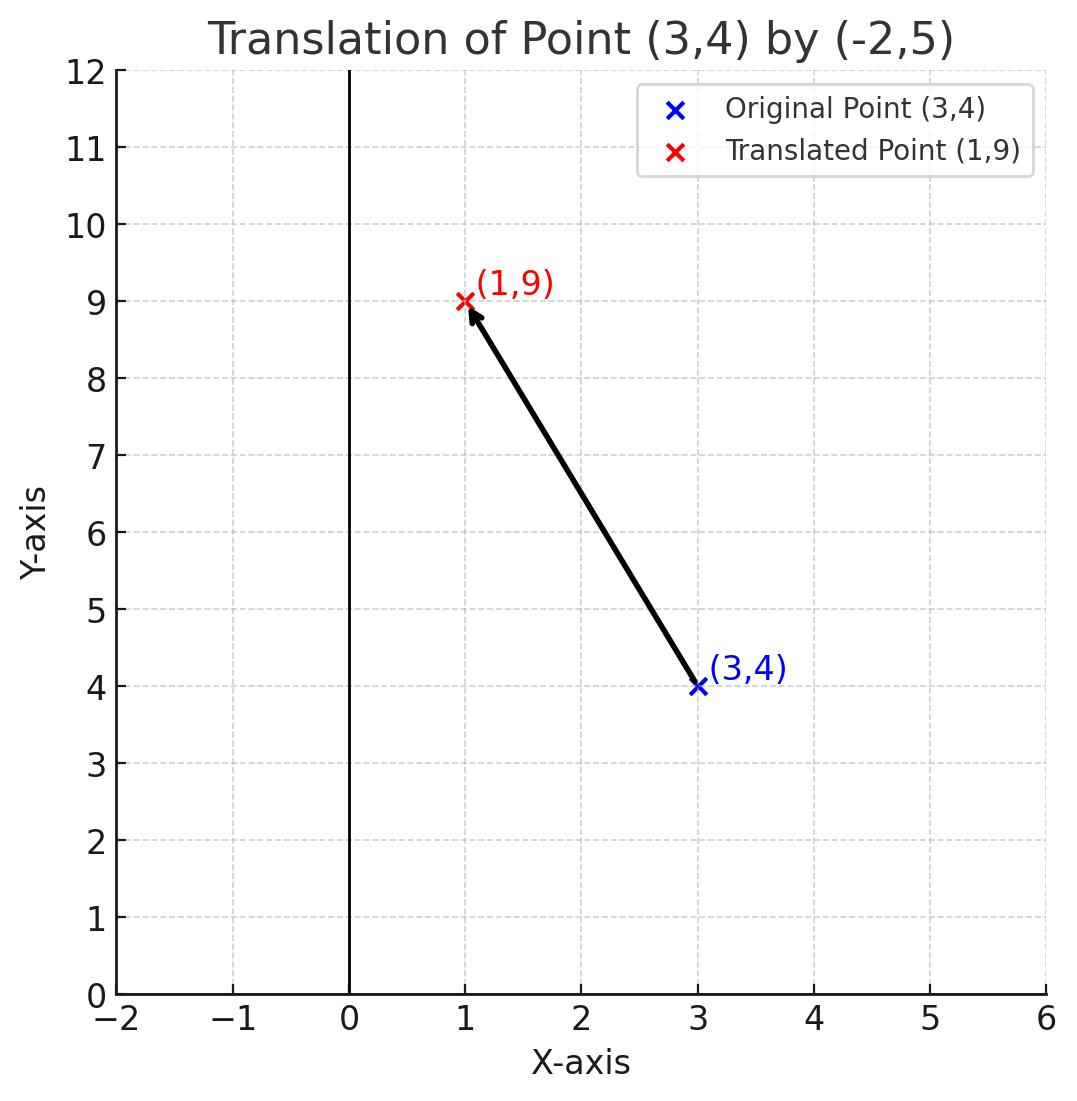
Example 2: Rotate the point \((2,3)\) by \(90^\circ\) counterclockwise about the origin.
Solution:
Using the \(90^\circ\) rotation formula: \[ (x', y') = (-y, x). \] \[ (x', y') = (-3,2). \]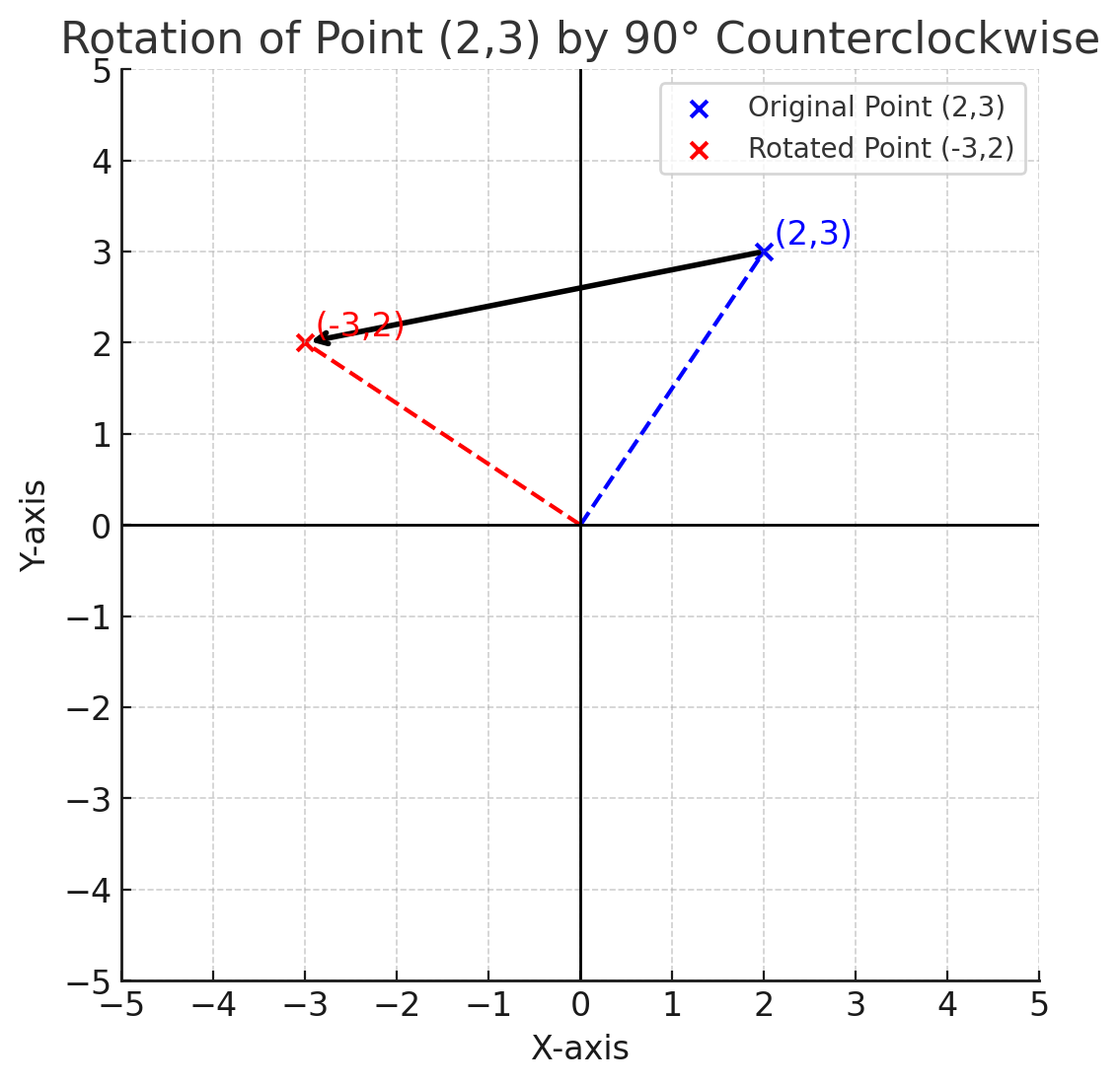
Example 3: Reflect the point \((5, -2)\) across the \(y\)-axis.
Solution:
Reflection over the \(y\)-axis: \[ (x', y') = (-x, y). \] \[ (x', y') = (-5, -2). \]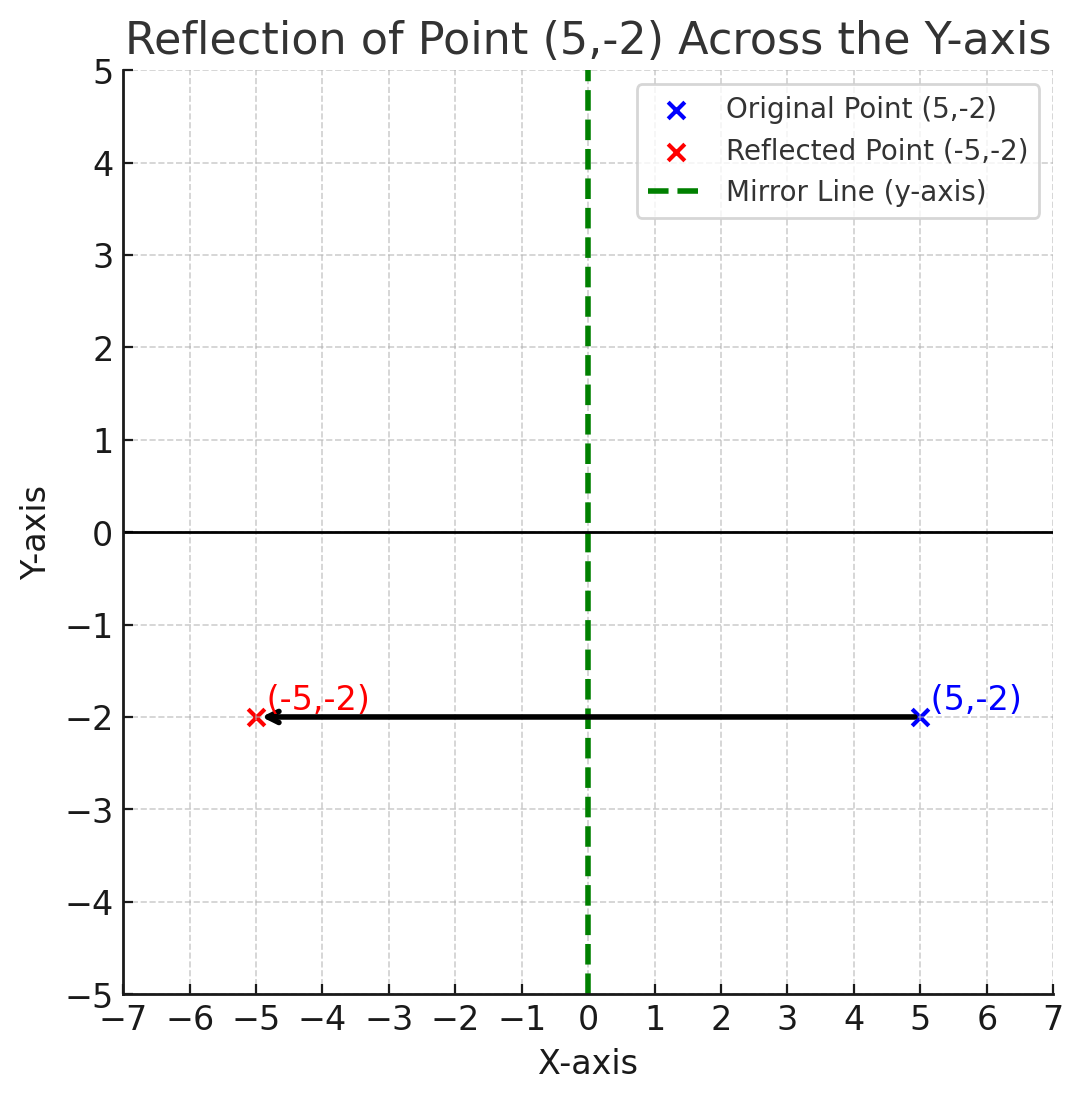
Example 4: Enlarge the point \((2, 3)\) by scale factor \(k=2\) about the origin.
Solution:
Using the enlargement formula: \[ (x', y') = (kx, ky). \] \[ (x', y') = (2 \times 2, 2 \times 3) = (4,6). \]
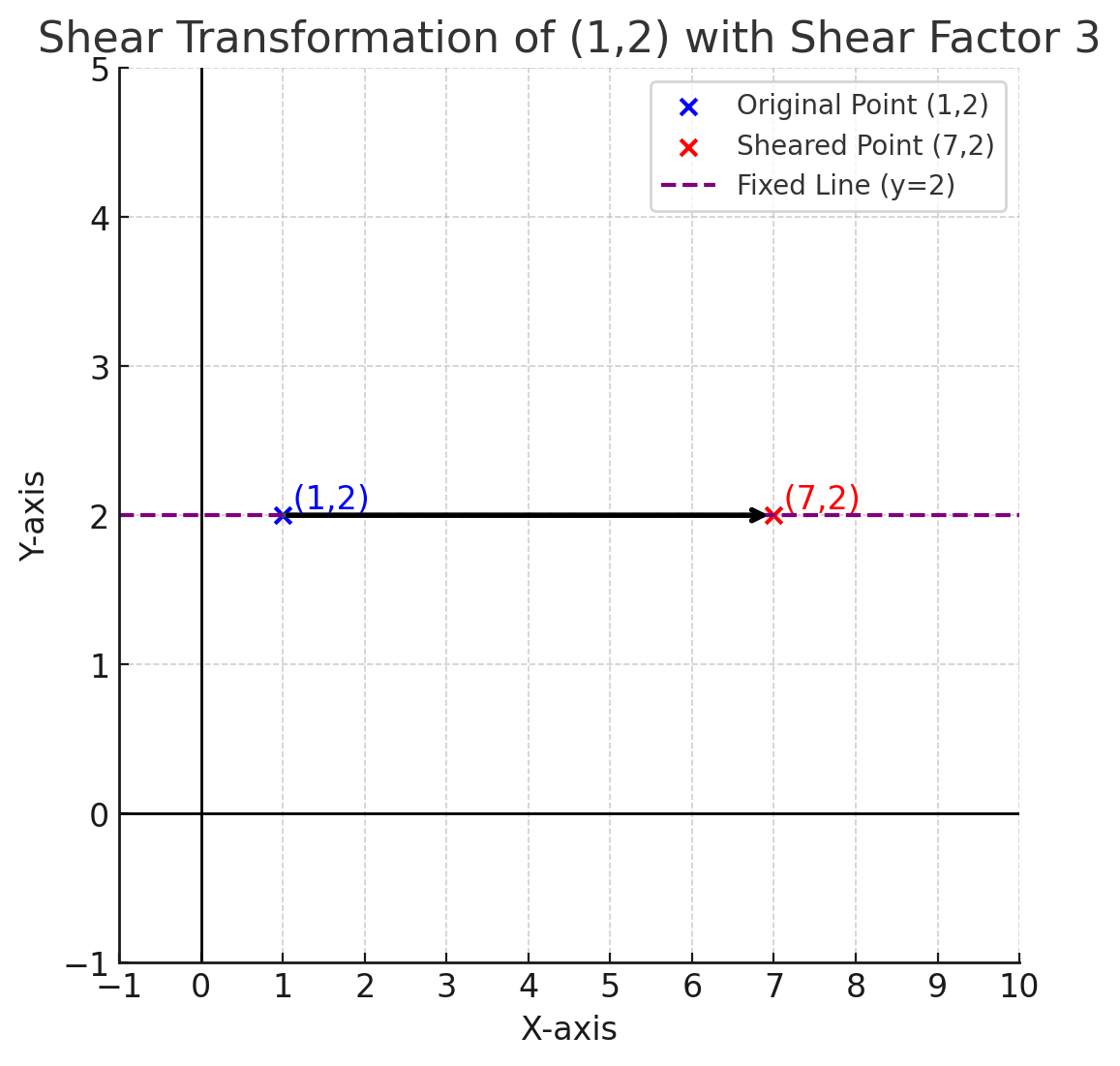
Example 5: Apply a shear transformation with shear factor \(k=3\) along the \(x\)-axis to the point \((1,2)\).
Solution:
Using the shear formula: \[ (x', y') = (x + ky, y). \] \[ (x', y') = (1 + 3(2), 2) = (7,2). \]