4.2 Sine and Cosine Rules
The sine and cosine rules are used to find unknown sides and angles in non-right-angled triangles.Key Concepts:
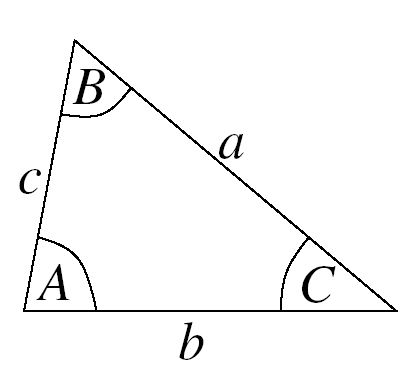
-
Sine Rule:
Used when given:- Two angles and one side (AAS or ASA).
- Two sides and a non-included angle (SSA).
-
Cosine Rule:
Used when given:- Two sides and the included angle (SAS).
- Three sides (SSS) when finding an angle.
Examples:
Example 1: Find the length of side \(c\) in a triangle where \(a = 7\) cm, \(b = 9\) cm, and \(\angle C = 120^\circ\).
Solution:
Step 1: Use the cosine rule: \[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\cos C. \] Substituting values: \[ c^2 = 7^2 + 9^2 - 2(7)(9)\cos 120^\circ. \] Since \(\cos 120^\circ = -\frac{1}{2}\): \[ c^2 = 49 + 81 - 2(7)(9) \times \left(-\frac{1}{2} \right). \] \[ c^2 = 49 + 81 + 63 = 193. \] \[ c = \sqrt{193} \approx 13.9 \text{ cm}. \] Thus, \(c \approx 13.9\) cm.Example 2: Find angle \(B\) in a triangle where \(a = 8\) cm, \(b = 10\) cm, and \(c = 12\) cm.
Solution:
Step 1: Use the cosine rule to find \(\cos B\): \[ \cos B = \frac{a^2 + c^2 - b^2}{2ac}. \] Substituting values: \[ \cos B = \frac{8^2 + 12^2 - 10^2}{2(8)(12)}. \] \[ \cos B = \frac{64 + 144 - 100}{192} = \frac{108}{192}. \] \[ \cos B = 0.5625. \] Step 2: Find \(B\) using inverse cosine: \[ B = \cos^{-1}(0.5625) \approx 55.2^\circ. \] Thus, \(\angle B \approx 55.2^\circ\).Example 3: Find the missing side \(a\) in a triangle where \(A = 40^\circ\), \(B = 75^\circ\), and \(b = 15\) cm.
Solution:
Step 1: Find angle \(C\): \[ C = 180^\circ - A - B = 180^\circ - 40^\circ - 75^\circ = 65^\circ. \] Step 2: Use the sine rule: \[ \frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B}. \] Substituting values: \[ \frac{a}{\sin 40^\circ} = \frac{15}{\sin 75^\circ}. \] Solving for \(a\): \[ a = \frac{15 \times \sin 40^\circ}{\sin 75^\circ}. \] \[ a \approx \frac{15 \times 0.6428}{0.9659} = \frac{9.642}{0.9659} \approx 9.99 \text{ cm}. \] Thus, \(a \approx 10.0\) cm.